Introduction
The strip chart has long served as a critical tool across various industries, from healthcare to manufacturing and scientific research. Known for tracking real-time data over extended periods, strip charts enable professionals to make quick, informed decisions by visualizing trends and changes. This comprehensive guide explores everything about strip charts, including their purpose, types, benefits, and applications in today’s data-driven landscape. If you’re interested in understanding how to select, set up, and utilize a strip chart to its fullest, read on for a complete breakdown.
Table of Contents
What is a Strip Chart?
A strip chart is a data-recording instrument designed to display continuous data trends on a moving strip of paper or a digital interface. The concept is simple: data points are plotted over time, allowing users to monitor changes in variables like temperature, pressure, and voltage. Traditionally, strip charts were paper-based with mechanical pens recording each data point. Today, digital strip charts offer advanced features, including remote monitoring, enhanced storage, and real-time analysis.
Used in fields ranging from healthcare and meteorology to manufacturing and power monitoring, strip charts help professionals visualize patterns and anomalies that may otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, medical practitioners often use strip charts to monitor patient heart rates, while engineers leverage them to oversee machine performance and ensure safety standards.

Types of Strip Charts
Understanding the various types of strip charts can help you choose the one that best meets your needs. Here’s a breakdown:
- Paper-Based Strip Chart: The traditional strip chart where a pen traces data points on a moving paper strip. Common in settings that require basic data visualization.
- Digital Strip Chart: Modern digital strip charts display data on a screen, providing the flexibility to store data, zoom in on specific time frames, and monitor remotely.
- Multi-Channel Strip Chart: Capable of recording multiple data streams simultaneously, these charts are ideal for comparing data variables in complex processes.
Importance of Strip Charts in Data-Driven Industries
Strip charts are indispensable in industries where continuous monitoring and timely interventions are essential. Here’s why they’re so valued:

Enhanced Data Visualization: By representing real-time data visually, strip charts offer a quick, comprehensive view of trends and fluctuations.
Improved operational safety: They alert operators to anomalies, such as rising temperatures in industrial machinery, allowing for immediate action.
Precision in Medical Monitoring: Medical strip charts, like those used in ECG, provide critical insight into a patient’s health status in real-time.
Environmental Tracking: In meteorology and environmental science, strip charts record temperature, humidity, and pressure trends, offering valuable data for research and forecasting.
How Strip Charts Function
Strip charts measure data over time, with the X-axis typically representing time intervals and the Y-axis displaying the recorded variable (e.g., temperature or voltage). Paper-based strip charts use a moving paper strip and a mechanical pen that marks data as it’s recorded. Digital strip charts, however, are fed data from sensors, converting it into real-time visual representations. This instantaneous feedback loop enables prompt responses to any abnormal trends or patterns.
Advantages of Using Strip Charts
Strip charts offer many benefits, particularly in environments that require constant data tracking. Here’s how they support improved data analysis:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Live tracking of critical metrics allows users to respond instantly to any anomalies or sudden changes.
- Long-Term Data Storage: Many digital strip charts store historical data, making it easy to analyze long-term trends and changes over time.
- Multi-Channel Recording: Simultaneously monitoring multiple data streams enhances operational efficiency by allowing users to cross-compare metrics.
- Simple Data Interpretation: Their straightforward, linear visuals make strip charts accessible to users with various technical skills.
Applications of Strip Charts in Key Industries
Strip charts play a pivotal role in a range of sectors:
- Healthcare: Used in hospitals to monitor heart rates, blood pressure, and other vital signs continuously.
- Manufacturing: employed to track machine performance metrics, such as temperature and pressure, ensuring smooth operations.
- Weather Forecasting: Essential in tracking environmental variables over time, like temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
- Power Generation: Provides real-time data on voltage and current, helping operators maintain optimal conditions in power plants.
- Chemical Laboratories: Monitors reaction rates and other parameters, crucial in research and experimental processes.
Choosing the Right Strip Chart for Your Needs
Selecting a strip chart involves evaluating several key factors:
Purpose and Channel Requirements: Consider whether you need a single or multi-channel model.
Format: Paper-based charts are simple but limited, while digital options offer flexibility and storage capabilities.
Resolution and Accuracy: The chart should meet the necessary precision levels required for your specific application.
Data Storage Needs: Opt for digital models if you require extensive data storage for long-term analysis.
User-Friendliness: Look for models that align with your team’s technical skills, ensuring easy operation and data interpretation.
Setting Up and Operating a Strip Chart
Using a strip chart effectively begins with proper setup and calibration:
Install and Connect Sensors: Attach sensors to the monitored equipment or area.
Connect and Configure the Chart: Ensure the chart receives data from the sensors, and set the time interval for data collection.
Monitor Real-Time Data: Keep an eye on the chart for any signs of irregularities or sudden shifts.
Analyze and Report: Use stored data for future reporting, trend analysis, and historical comparisons.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips for Strip Charts
Proper maintenance is essential for accurate, consistent data recording. Here’s how to keep your strip chart functioning optimally:
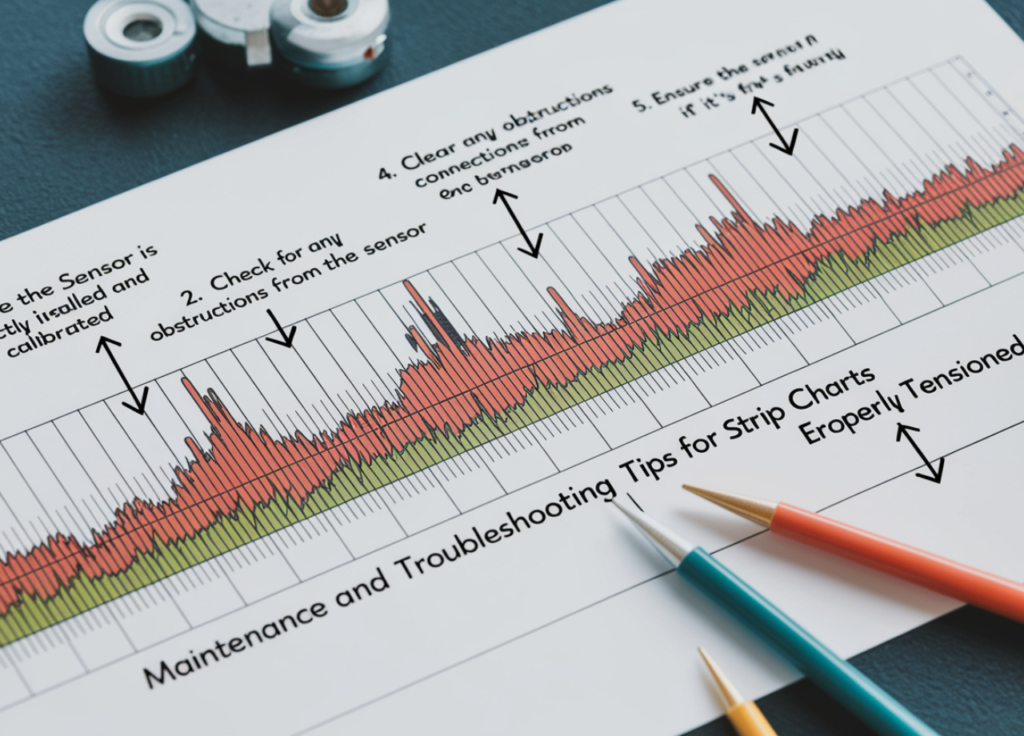
- Paper-Based Strip Charts:
Keep ink levels and paper rolls stocked.
Clean the writing mechanism regularly to prevent data skips.
Calibrate the machine to maintain alignment with sensors. - Digital strip charts:
regularly update software and firmware.
Ensure sufficient storage capacity for data.
Perform routine sensor checks to verify accuracy.
Using Strip Charts for Effective Data Analysis
Strip charts are valuable for both immediate monitoring and in-depth analysis. Here’s how to maximize their analytical benefits:
- Identifying Trends: Observe gradual shifts in data, such as rising temperatures, to anticipate issues.
- Spotting anomalies: Detect irregularities or outliers, allowing for rapid intervention.
- Comparing Variables: Multi-channel charts enable direct comparisons between different data points, like voltage and temperature, essential in industrial quality control.
- Report Generation and Forecasting: Export data for detailed analysis, using historical data to forecast future conditions, like predicting machinery maintenance needs.
Advantages and drawbacks of strip charts
While highly beneficial, strip charts come with both pros and cons:
- Advantages:
Continuous recording, suitable for long-term monitoring.
User-friendly, with clear visual data representation.
Real-time feedback for immediate decision-making.
Multi-channel capability for enhanced data insights. - Disadvantages:
Paper-based models require consumables like ink and paper.
Limited data transfer options in paper models.
Sensor accuracy is crucial, as chart accuracy depends on reliable sensor data.
Initial setup and calibration require precision.
The Future of Strip Charts
The future of strip charts is bright, with technological advancements continually improving functionality and data integration. Innovations likely to shape the future of strip charts include:
- Wireless Connectivity: streamlined setup and data transfer, reducing the need for complex wiring.
- AI-Driven Analytics: Using artificial intelligence to detect patterns and forecast issues, paving the way for predictive maintenance.
- Cloud Integration: Cloud-based storage and access will enable remote monitoring and data sharing.
- Sustainable Materials: Eco-friendly options are expected to become the norm, especially in paper-based charts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, strip charts remain a vital tool in today’s data-focused world. From monitoring patient vitals in hospitals to overseeing temperature fluctuations in factories, these devices provide invaluable real-time insights. As digital technologies continue to enhance their capabilities, strip charts are evolving to meet modern demands, offering advanced features like multi-channel tracking, cloud integration, and predictive analytics. By selecting the right model, setting it up effectively, and maintaining it properly, you can maximize the potential of strip charts in any industry.
You can see latest update on: Legwarmers